Handleiding voor UTM-tagging op je Google bedrijfsprofiel
Title
Title
Step 3: Internal and external linking
Links, you know them. The clickable pieces of text that take you to another page on the website (internal links) or to a completely different website (external links). A healthy link structure and the authority you build with it are part of link building. During an SEO audit, it is only a small effort to also verify the following things:
- Broken links: these are links that no longer work, for example, because the page no longer exists. Remove or adjust to a proper destination!
- Pages with too many outgoing links: if there are too many external links on a page, alarm bells start ringing at Google. This is because it may indicate link exchange where you exchange links to your own website for a link to another website. In principle, this is against the rules of the search engine. So be careful with the amount of external links.
- Dofollow links: if a link has a dofollow tag, the link passes value to the destination page. Don't want to pass on value? Then add a nofollow tag.
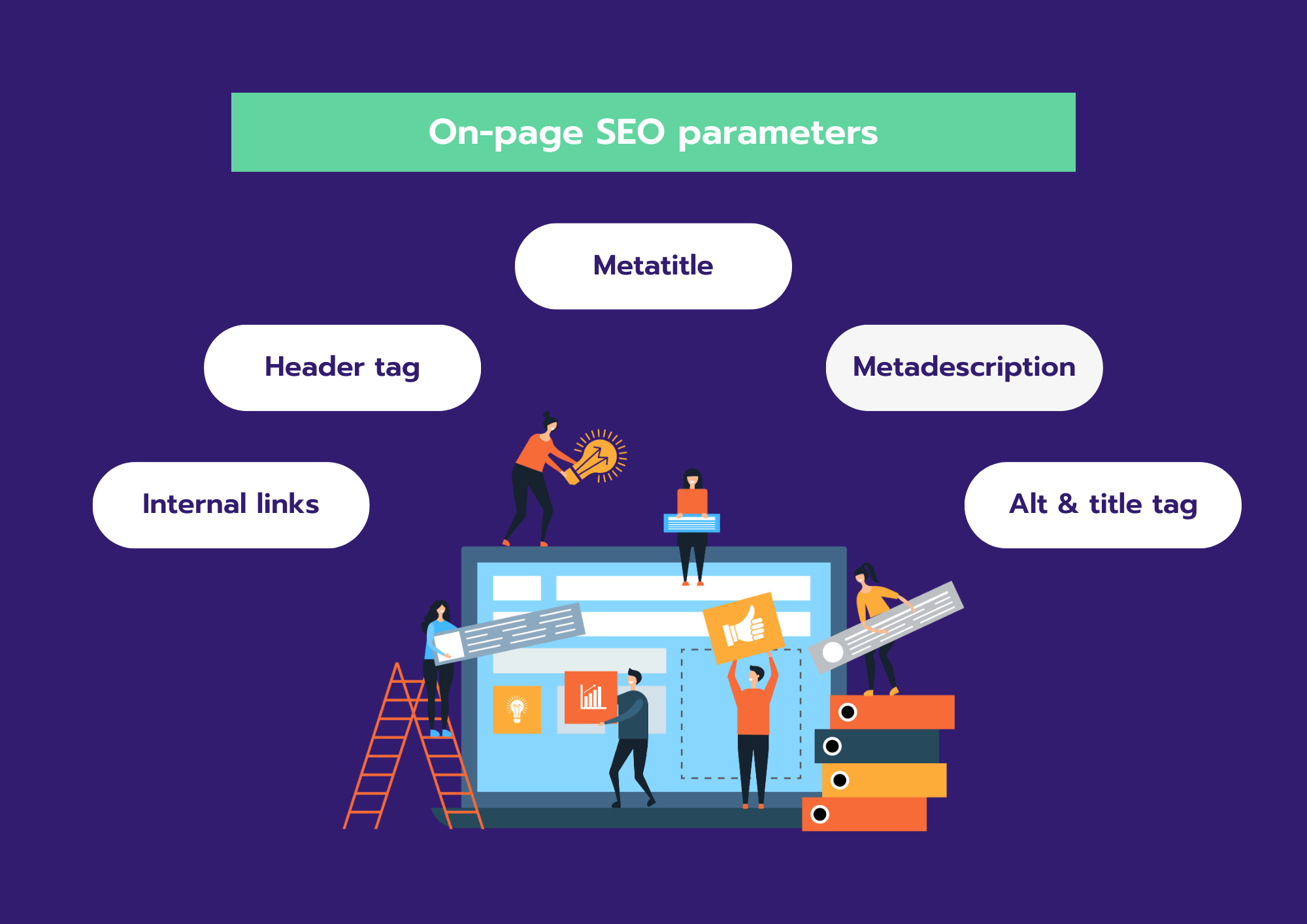
Step 4: On-page SEO parameters
On-page SEO parameters are snippets of code on a web page. They are not visible to the visitors of that page, but they are visible to search engines. The most important parameters are the metatitle and the metadescription.
- Header tag: also called H1. It is the title of the text on a web page. There should be only one H1 on the entire page. Subtitles, denoted by H2 through H6, are allowed to appear multiple times. When auditing, also check that the H1 is not too long. Preferably no longer than 60 characters.
- Meta title: this is the title that appears in the SERPs and leads to the page in question. Also make sure that it is not too long and that it includes a relevant keyword.
- Meta description: this is the text snippet below the meta title in the search results. A common mistake is that the text snippet is too long and therefore gets hyphenated by Google. So make sure the description is the right length (150 characters) and choose a unique text, not one you use for every page.
In the H1, meta title and description, it is recommended to use relevant keywords. You normally already have these at hand thanks to a thorough keyword research.
Step 5: Optimize images
Images on web pages play an important role for your technical SEO. Google is not yet ready for its algorithm to analyze and interpret image content. Therefore, we add a title and alt text. This is how they provide the search engine with a description of the image. Here's what to pay attention to:
- No optimized title: the title, or file name, must match the content of the images. Automated file names from a smartphone or camera are out of the question.
- Broken images: when the image does not work properly, an error message appears. Delete the image or replace it with one that does work.
- Alt text: when the image does not work, a short description of what exactly is in that image will still appear. That description is called the alt text. Alt texts that are meaningless are best avoided. They describe what is in the image and contain relevant keywords. That helps the visitor understand your page.
Step 6: Multiple languages
If you have pages in different languages, indicate that by adding Hreflang tags. For example, if you offer a page in Dutch, French and English on a Belgian website. It is a piece of code that indicates which language applies to that page. Things might also go wrong with the Hreflang, so check the following during the SEO audit:
- Incorrect language codes
- Missing return links
- Invalid urls
- Non-canonical pages with Hreflang elements
- Conflicting and incomplete Hreflang elements
Title
Title
Step 7: Core web vitals and user experience
Google monitors a number of signals regarding the user experience of your site. Consider page speed, mobile friendliness and security. These are some examples of core web vitals. Core web vitals are an important ranking factor and therefore should not be missing from your technical SEO audit.
- Page speed: page speed logically indicates how long the page takes to load. You can easily measure this via Pagespeed Insights. Handy: you get a score for both the desktop and mobile versions of your website.
- Security: with safe browsing, Google is committed to contributing to a safe World Wide Web. The search engine detects malware on your site and checks that you are using the latest website and server software.
- Https: Due to the encrypted information transmission of the https protocol, important info such as your name, bank account and phone number, is harder to steal. The configuration of this protocol is extremely important.
- Mobile friendliness: through this test from Google, you check if a website is suitable for mobile devices. Do components load fast enough? Are clickable buttons spread far enough apart? Are all images optimized? The design of the mobile version must be fully optimized for a mobile device.
- Intrusive elements: disruptive pop-ups (with the exception of mandatory pop-ups like the cookie banner) are a sign of poor user experience for Google. If you do opt for a pop-up, make it appear only once. It should be easy to close and hide only part of the content.
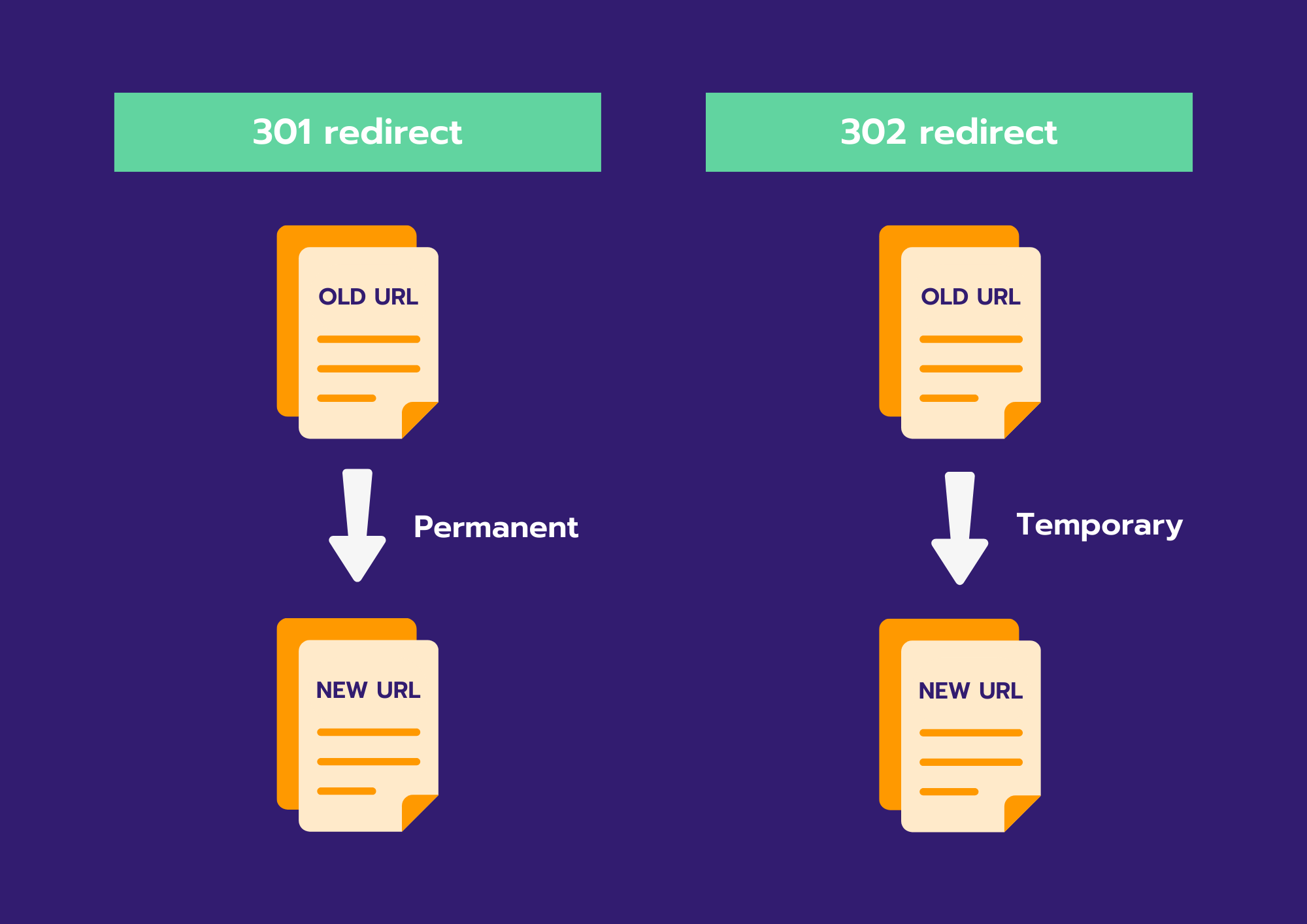
- 302 redirects: this type of redirects are temporary, so they do not forward link value. Is a page permanently deleted? Then you should use the next type of redirect.
- 301 redirects: this is the type to permanently redirect old urls to new ones. With this you do pass link value. When doing an audit it is very important to check these redirects. Mistakes here are detrimental to your SEO.
- Redirect chain: if you redirect to a page that has also been redirected, you create a redirect chain. This results in a longer page load time and is not ideal for indexing by Google. Instead of creating a chain, refer directly to the correct page.
